What is a Switch?
A Switch is a networking device that
Switches data packets between devices on the same network (or same LAN -Local Area Network).
-Switch is a Layer2 device.
————————————————————————————–
What is Switching?
The function of Switching is to
Switch data packets between devices on the same network (or same LAN -Local Area Network).
————————————————————————————–
What is a router?
A Router is a networking device that
Routes packets between different networks (between different LANs – Local Area Networks).
-Router is a Layer3 device.
————————————————————————————–
What is Routing?
The function of Routing is to
Route packets between different networks (between different LANs – Local Area Networks).
————————————————————————————–
What are the diff types of ports of a Router?
1. Data Ports- Fast Ethernet (for LAN’s) ; Serial(for WAN’s)
2. Virtual Ports- Loopback, VTY ports
3. Management Ports- Console, Auxiliary
————————————————————————————–
What are the diff ways to manage a ROUTER?
A>Non-Network
Console Port:- By connecting the router’s console port to a workstation through a console cable.
The console port is the management port which is used by administrators to log into a router directly-that without using a network connection. You require a terminal emulator application like hyperterminal or PuTTY to connect to router.
Auxiliary Port:- By using a remote computer through a modem that calls another modem connected to the router with a cable using the Auxiliary Port on the router.
Auxiliary Port (AUX Port) allows a direct, non-network connection to the router, from a remote location.
B>Over the Network
The routers can be managed over the network by using standard TCP/IP protocols like Telnet, SSH, HTTP or HTTPS.
Telnet:- A Telnet client and server application ships with Cisco’s IOS software.
SSH:- SSH is a more secure way to configure routers, since the SSH communication is encrypted.
HTTP or HTTPS:- Cisco IOS also has a HTTP server to managed web based communication with the router.
What type of Cable is used to Manage a Router or Switch using Console Port?
Router or Switch end has a RJ45 port used as console port and a Serial/COM port of a Computer are connected by a Roll-Over Cable.
Roll-Over Cable :- One end of the cable is RJ45 type and a DB9 to RJ45 converter is molded on the other end.
————————————————————————————–
What are the diff types of router memory?
ROM, Flash Memory, NVRAM, RAM
ROM– Instructions for POST, Bootstrap program, Mini-IOS is stored here
Flash Memory– IOS is stored here
NVRAM– Start up Configuration file: startup-config is stored here
RAM– Running configuration file: running-config is stored here
————————————————————————————–
What should be the value of Configuration Register for Bootstrap to load IOS from FLASH?
0x2102
————————————————————————————–
What is Bootstrap program responsible for?
The Bootstrap program is responsible for
1.Initializing hardware
2.Finding where IOS program is located and then
3.Loading IOS image
————————————————————————————–
What are the possible locations of IOS image?
FLASH, TFTP Server
————————————————————————————–
What is ROM Monitor?
If the Bootstrap program is not able to find a valid IOS image, it will act as ROM Monitor.
————————————————————————————–
What can be done with ROM Monitor?
ROM Monitor is capable of providing a command line environment that can be used to perform certain configuration tasks, such as
-Downloading IOS image using TFTP
-Recovering a lost password
-Changing the configuration register value etc.
————————————————————————————–
What is Unicast?
- It is a One to One Communication.
- Unicast is a type of communication, where there is only one sender & one receiver.
Example:
1) Browsing a website. (Webserver is the sender and your computer is the receiver.)
2) Downloading a file from a FTP Server. (FTP Server is the sender and your computer is the receiver.)
What is Multicast?
- It is a One to Many communication.
- In Multicast, the sender transmit only one copy of data and it is delivered and/or processed to many devices who are interested in that traffic(Not as delivered and processed by all devices as in Broadcast).
- Devices which are interested in a particular Multicast traffic must join to that Multicast group to receive the traffic.
- IP Multicast Groups are identified by Multicast IP Addresses (IPv4 Class D Addresses)
Example :
Multicast Windows Deployment Services (WDS) OS deployment traffic, IP TV etc
————————————————————————————–
What is Broadcast?
- In Broadcast, there is only one sender and the data is sent only once. But the Broadcast data is delivered to all connected devices.
- Switches by design will forward the broadcast traffic and Routers by design will drop the broadcast traffic.
Example:
1) ARP Request message,
2) DHCP DISCOVER Message
————————————————————————————–
What are the different modes in Router?
1.User Mode; 2.Privilege Mode; 3.Global Configuration Mode;
Each Mode has access to different set of IOS commands.
————————————————————————————–
What is the command to enter PRIVILEGE mode from USER mode?
>enable
————————————————————————————–
What is the command to enter Global Configuration mode from PRIVILEGE Mode?
#configure terminal
————————————————————————————–
What are the sub modes of Global configuration mode?
1.Interface Mode(Router physical interface configuration mode):-
Router(config-if)
2.Sub Interface Mode(Router sub-interface configuration mode):-
Router(config-subif)#
3.Line Mode(Router line configuration mode – console, vty etc):-
Router(config-line)#
4.Router Configuration Mode(Routing protocols configuration mode):-
Router(config-router)#
————————————————————————————–
What is the command to backup IOS to TFTP server and in which mode it is done?
In Privilege Mode.
The command is :- #copy flash tftp
————————————————————————————–
What is the command to backup running configuration to TFTP server and in which mode it is done?
In Privilege Mode.
The command is:- #copy running-config tftp
————————————————————————————–
What is the command to Reboot a Router?
#reload
————————————————————————————–
What is the command to erase the contents of Flash?
#erase flash
————————————————————————————–
What is the command to upgrade IOS from a TFTP server?
#copy tftp flash
————————————————————————————–
What is to be done in order for the router to use the newly copied IOS image from TFTP to Flash?
The Router has to Reboot to use the newly copied IOS Image.
————————————————————————————–
What is a Static Route?
A static route is a route that is manually configured on the router by a network administrator.
————————————————————————————–
What is Default Route?
v A Default Route (also known as the gateway of last resort) is a special type of static route.
v Where a static route specifies a path a router should use to reach a specific destination, a default route specifies a path the router should use if it doesn’t know how to reach the destination.
v Default Route is the network route used by a router
when there is no other known route exists for a given IP datagram’s destination address.
All the IP datagrams with unknown destination address are sent to the default route.
————————————————————————————–
What is a Dynamic Route?
Dynamic routes are routes that a router learns by using a routing protocol. Routing protocols will learn about routes from other neighboring routers running the same routing protocol.
————————————————————————————–
What is a Routed Protocol?
A Routed Protocol is a network protocol which carries data from one network to another network. Routed Protocol carries user traffic such as e-mails, file transfers, web traffic etc.
Examples:- IP (Internet Protocol), IPX (Internetwork Packet Exchange) and AppleTalk
————————————————————————————–
What is Routing Protocol?
Routing Protocols learn the routes (network paths) and provide the best routes (network paths) from one network to another network.
Examples: – RIP (Routing Information Protocol) , EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First).
————————————————————————————–
What is an Autonomous System?
An Autonomous System (AS) is a group of networks under a single administrative control which could be an Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a large Enterprise Organization.
————————————————————————————–
What is an Autonomous System number (ASN)?
An Autonomous System Number (ASN) is a 32-bit binary number used to identify the Autonomous Systems.
v 32-bit (4-Octet) AS numbers are represented as either as simple integers,
or in the form x.y, where x and y are 16-bit numbers.
v 32-bit Autonomous System Number (ASN) is also known as 4-Octet Autonomous System Number (ASN).
————————————————————————————–
What is IGP?
An Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) refers to a routing protocol that handles routing within a single autonomous system.
IGPs include RIP, IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF.
OR
Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) is a Routing Protocol which is used to find network path information within an Autonomous System.
————————————————————————————–
What is EGP?
An Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) refers to a routing protocol that handles routing between different Autonomous Systems (AS).
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an EGP.
OR
Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) is a Routing Protocol which is used to find network path information between different Autonomous Systems.
————————————————————————————–
What is Administrative Distance (AD)?
Administrative Distance is the trust worthiness Or the reliability of a routing protocol.
Administrative Distance (AD) is a value that routers use
in order to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from two different routing protocols.
————————————————————————————–
What are the Range of AD values?
0 to 255
v A smaller Administrative Distance (AD) is more trusted by a router, therefore the best Administrative Distance being 0 and the worst, 255.
| Routing Protocol | Administrative Distance Value | |
| Connected Interface | 0 | |
| Static | 1 | |
| EIGRP | 90 | |
| IGRP | 100 | |
| OSPF | 110 | |
| IS-IS | 115 | |
| RIP | 120 |
————————————————————————————–
What is the Syntax for Static Route?
Router(config)#ip route <Dest. Network> <SubnetMask> <NextHop>
————————————————————————————–
What are the advantages of Static Routing?
v Reduced routing protocol router overhead
v Reduced routing protocol network traffic.
————————————————————————————–
What are the disadvantages of Static Routing?
v Network changes require manual reconfiguration in routers
v Network outages cannot be automatically routed around.
v Also it is difficult to configure static routing in a complex network.
————————————————————————————–
What is Distance-Vector Routing Protocol?
- Ø Distance vector routing protocols use the distance and direction (vector) to find paths to destinations.
- Ø A router which is running a Distance Vector routing protocol informs its neighbors about the network topology changes periodically.
Examples:
- Routing Information Protocol Version1 (RIPv1)
- Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
————————————————————————————–
What is Link-State Routing Protocol?
- Ø Each router running a link state routing protocol originates information about the router, its directly connected links, and the state of those links. This information is sent to all the routers in the network as multicast messages.
- Ø Link-state routing always try to maintain full networks topology by updating itself incrementally only whenever a change happen in network.
Examples:
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS)
————————————————————————————–
What is Hybrid Routing Protocol?
A Hybrid Routing protocol has the advantages of both Distance Vector and Lin k State Routing protocols and merges them into a new protocol.
v (EIGRP) sends traditional Distance Vector updates
v (EIGRP) has Link State characteristics also. It synchronizes routing tables between neighbors at startup, and then it sends specific updates only when a network topology change happens.
Examples:
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
- Routing Information Protocol Version2 (RIPv2)
————————————————————————————–
What is Metric?
v If the router has more than one route found by two different routing protocols, for the same destination network, the router chooses Administrative Distance to choose the best one.
v But in some cases, there will be two paths found by the same protocol, to the same destination network.
v Here the Routing Protocol will use Route Metric value to find the best path. For every protocol there is a parameter used
RIP – Hop Count; IGRP & EIGRP – Bandwidth, Delay, Reliability & Load; OSPF, IS-IS – Cost.
————————————————————————————–
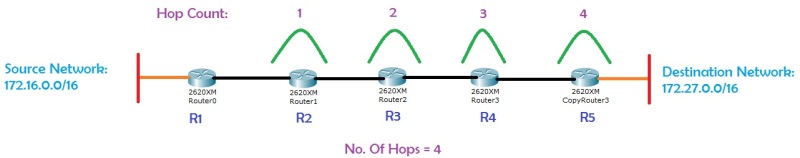
What is Hop Count?
Hop count is the number of routers (number of hops) from the source router through which data must pass to reach the destination network.
————————————————————————————–
What is Bandwidth?
The data capacity of a link in Kbps.
————————————————————————————–
What is Delay?
The Time it takes to reach the destination.
————————————————————————————–
What is Reliability?
The path with the least amount of errors or downtime.
————————————————————————————–
What is Load?
The amount of utilization of a path.
Or
The amount of activity on a network resource, such as a router or link
————————————————————————————–
What is MTU?
The IEEE 802.3 specification limits the data portion of the 802.3 frame to a maximum of 1500 bytes. The Data field was designed to hold Layer 3 packets; the term maximum transmission unit (MTU) defines the maximum Layer 3 packet that can be sent over a medium. Because the Layer 3 packet rests inside the data portion of an Ethernet frame, 1500 bytes is the largest IP MTU allowed over an Ethernet.
————————————————————————————–
What are the Metrics for diff Routing Protocols?
| Protocol | Metric | Explanation |
| RIP | Hop Count | Number of routers (number of hops) from the source router through which data must pass to reach the destination network. |
| OSPF | Cost | Measurement in the inverse of the bandwidth of the links |
| EIGRP | Bandwidth | The capacity of the links in Kbps (T1 = 1554) |
| EIGRP | Delay | Time it takes to reach the destination |
| EIGRP | Load | The path with the least utilization |
| EIGRP | MTU | The path that supports the largest frame sizes |
| EIGRP | Reliability | The path with the least amount of errors or down time |
————————————————————————————–
What is Convergence?
If the network topology changes, for example a link fails the routers should react by advertising that some routes have failed, and pick a new current best route. This process is called convergence.
————————————————————————————–
What is Converged Network Topology?
A converged network topology means all the routers agree on which links are up, which links are down, which links are running fastest etc.
————————————————————————————–
What is Convergence Time?
Convergence time is the time which a group of routers reach the state of convergence.
————————————————————————————–
What is CDP?
- Ø CDP-Cisco Discovery Protocol is a proprietary protocol of CISCO to help administrators collect information about both locally attached and remote devices.
- Ø By using CDP, you can gather hardware and protocol information about neighbor devices, which is useful information for troubleshooting and documenting the network.
————————————————————————————–
What is the Command to see Cisco device neighbors?
To see the summary of Cisco device neighbors, run the “show cdp neighbors” IOS command from privilege mode.
————————————————————————————–
What is Null Interface?
v Null interfaces are virtual interfaces and are always up.
v Null interfaces never forward or receive traffic; packets routed to a null interface are dropped.
v Null interface is also known as bit bucket because the IP datagram reaching Null interface are dropped as soon as they are received.
v The Null interface in a Cisco Router is a mechanism for preventing routing loops. EIGRP creates a route to the Null0 interface when it summarizes a group of routes.