What is STP?
- Ø The function of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is to prevent Layer 2 switching loops and broadcast storms in a Local Area Network (LAN) because of redundant links.
- Ø STP allows redundant links in a network to prevent complete network failure if an active link fails.
———————————————————————————————————————–
Who developed STP?
- Ø Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is based on an algorithm, which was developed by Radia Perlman at DEC (Digital Equipment Corporation, now part of HP).
- Ø The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) was then standardized by IEEE as IEEE 802.1D.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is the reason for developing another version STP i.e. RSTP?
Because of the slow convergence time of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) IEEE 802.1D, another version of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP IEEE 802.1W) is developed, which is also known as Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), which has much better convergence time.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) frame?
- Ø The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) enabled switches in a redundant Local Area Network (LAN) need to exchange information between each other for Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to work properly.
- Ø Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are messages exchanged between the switches inside an interconnected redundant Local Area Network (LAN).
- Ø Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) frames contain information regarding the Switch ID, originating switch port, MAC address, switch port priority, switch port cost etc.
- Ø When Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are received, the Switch uses a mathematical formula called the Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) to know when there is a Layer2 Switch loop in network and determines which of the redundant ports needs to be shut down.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is the destination MAC address used by Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)?
Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) frames are sent out as multicast messages regularly at multicast destination MAC address 01:80:c2:00:00:00.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What are the different types of BPDUs?
Three types of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) are
- Configuration BPDU (CBPDU),
- Topology Change Notification (TCN) BPDU
- Topology Change Notification Acknowledgment (TCA) BPDU
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is the basic purpose of the BPDUs and STA?
The basic purpose of the Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) and the Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) is to avoid Layer2 Switching loops and Broadcast storms.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Configuration BPDU?
What is TCN BPDU?
What is TCA BPDU?
What is Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) Frame Format?
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Switch Priority Value (Bridge Priority)?
- Ø Every Switch Participating in a Spanning Tree Protocol network is assigned with a numerical value called Switch Priority Value.
- Ø Switch Priority Value is a 16-bit binary number.
- Ø The Switch Priority, which is a numerical value defined by IEEE 802.1D, which is equal to 32,768 by default.
- Ø Switch Priority value decides which Switch can become Root Bridge (Root Switch).
- Ø The Switch Priority value is used to find the Switch ID.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Switch ID (Bridge ID)?
- Ø Switch ID decides which Switch can become Root Switch. A Switch with lowest Switch ID will become the Root Switch.
The Switch ID (Bridge ID) is made from two values.
- Ø The Switch Priority which is a numerical value defined by IEEE 802.1D, which is equal to 32,768 by default.
- Ø The MAC Address of the Switch.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Root Switch (Root Bridge)?
- Ø The root bridge function is only for the spanning tree protocol.
- Ø The other switches refer to the root switch to find redundant paths so as to ensure NO Layer 2 Loops exist.
- Ø The main function of the root switch is to broadcast network topology changes to all the switches in the network.
- Ø When a switch detects a topology change (i.e., a trunk goes down) it sends a topology change notification (TCN) BPDU to the root switch. The root switch then broadcasts that topology change out to the other switches.
- Ø If each switch could broadcast change notifications to the other switches it would be total chaos.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Path Cost or Spanning Tree Path Cost value?
- Ø Spanning Tree Path Cost value can be defined as the accumulated port costs from a Switch to reach the Root Switch.
- Ø The Spanning Tree Cost Value is inversely proportional to the associated bandwidth of the path and therefore a path with a low cost value is more preferable than a path with high cost value.
The following table lists the Port Cost value for different bandwidths.
| Link Speed or Link Bandwidth | Cost Value | |
| 10 Gbps | 2 | |
| 1 Gbps | 4 | |
| 100 Mbps | 19 | |
| 10 Mbps | 100 |
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Root Port?
- Ø Once the Root Switch is elected, every other Switch in the network must select a single port on itself to reach the Root Switch.
- Ø The single selected port on a Switch with least Path Cost to reach the Root Bridge is called the Root Port.
- Ø Root Bridge (Switch) will never have a Root Port.
———————————————————————————————————————–
See the Diagram for Root Port
The above layout of Switches shows that Switch 4 has two ports to reach the Root Bridge. If there are multiple ports present in a Switch to reach the Root Bridge (Switch). Spanning Tree Protocol Algorithm must select the best port from them to reach the Root Bridge. Here the port with least path cost (4+4=8) is marked as Root Port.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Spanning Tree Port Priority?
Each port of a Switch has a Spanning Tree Port Priority value associated with it, which is equal to 128 by default.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is Spanning Tree Port ID?
- Ø Spanning Tree Port ID is formed by adding the 4-bit port priority value (the default value of 128) to 12-bit interface identifier (total 16 bits).
- Ø Normally, a Port ID is denoted in Hexadecimals similar as 0x8015, which is equivalent to 128.21 in decimals, where the first part is the default Port Priority number and second part is the switch interface identifier.
———————————————————————————————————————–
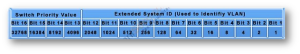
What is Extended System ID?
The Extended System ID is utilized by spanning-tree to include the VLAN ID information inside 16-bit STP Bridge Priority value. Extended System ID is the least significant 12-bits in 16-bit STP Bridge Priority value.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is PVST or PVST+?
Per-VLAN spanning tree protocol plus (PVST+) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that expands on the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) by allowing a separate spanning tree for each VLAN.
Cisco first developed this protocol as PVST, which worked with the Cisco ISL trunking protocol, and
then later developed PVST+ which utilizes the 802.1Q trunking protocol.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is PVST?
Cisco first developed a protocol that expands on the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) as PVST, which worked with the Cisco ISL trunking protocol.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is PVST+?
Cisco later developed PVST+ which utilizes the 802.1Q trunking protocol.
———————————————————————————————————————–
What is the working of PVST or PVST+?
By creating a separate spanning tree for each VLAN, data traffic from the different VLANs can take different paths across the network, as opposed to all switched traffic taking the same path. This can effectively create a load balancing situation and improve network efficiency.
By default the Cisco switches in Packet Tracer appear to be using PVST+ as the default implementation of spanning tree protocol.
———————————————————-
What is RSTP?
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an enhancement of the original STP 802.1D protocol. The RSTP 802.1w protocol is an IEEE open implementation.
——————————————————————————————————————–
What is Rapid-PVST+?
Cisco has its own proprietary implementation of RSTP, that includes the benefits of its Per-VLAN spanning tree protocols, called Rapid-PVST+.
——————————————————————————————————————–
What is the working of RSTP and Rapid-PVST+?
Rapid-PVST+ and RSTP are important enhancements to the original STP protocol because they can switch ports from blocking to forwarding without relying on timers, execute spanning tree calculations and converge the network faster than STP.
In STP, network convergence can take up to 50 seconds, with RSTP and Rapid-PVST+ network convergence can happen in just over 6 seconds.
——————————————————————————————————————–

Thanks
Very informative and helpful for networking interview.